Dressing
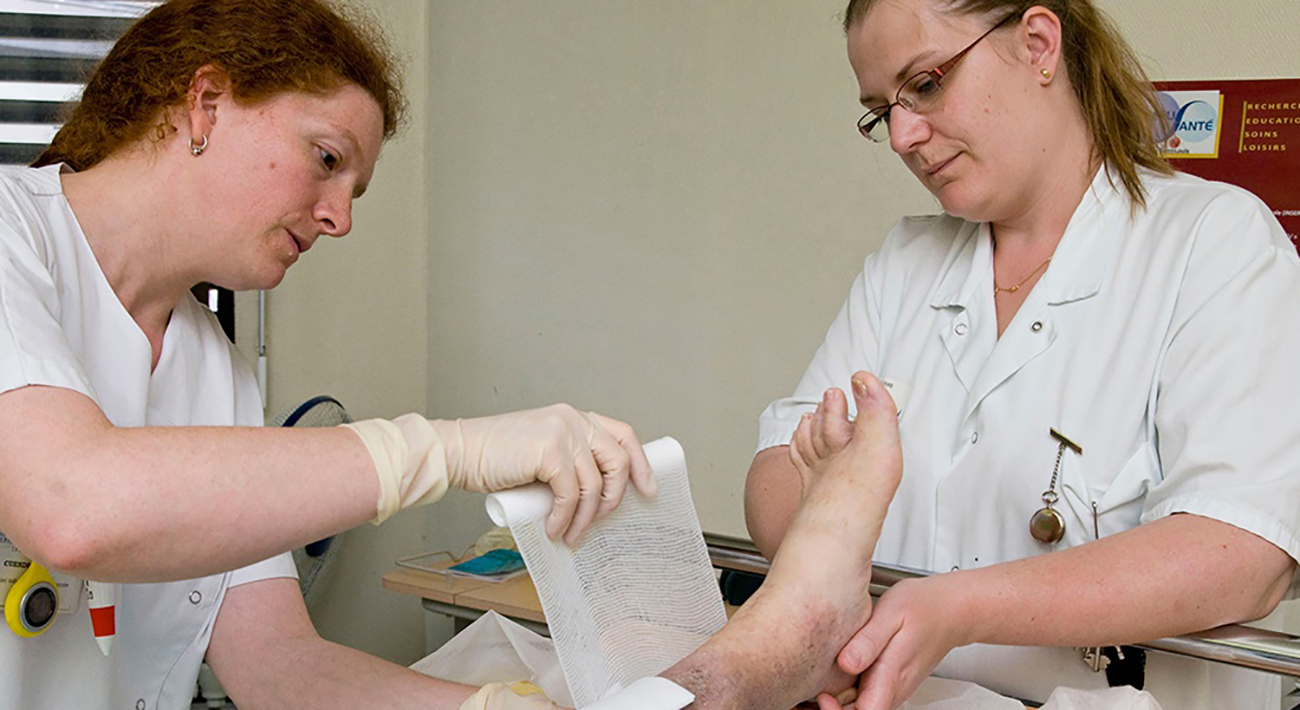
A dressing is a sterile pad or compress applied to a wound to promote healing and protect the wound from further harm. A dressing is designed to be in direct contact with the wound, as distinguished from a bandage, which is most often used to hold a dressing in place.
Medical uses
A dressing can have a number of purposes, depending on the type, severity and position of the wound, although all purposes are focused towards promoting recovery and protecting from further harm. Key purposes of a dressing are:
- Stem bleeding – to help to seal the wound to expedite the clotting process;
- Protection from infection – to defend the wound against germs and mechanical damage;
- Absorb exudate – to soak up blood, plasma, and other fluids exuded from the wound, containing it/them in one place and preventing maceration;
- Ease pain – either by a medicated analgesic effect, compression or simply preventing pain from further trauma;
- Debride the wound – to remove slough and foreign objects from the wound to expedite healing;
- Reduce psychological stress – to obscure a healing wound from the view of the patient and others.
Ultimately, the aim of a dressing is to promote healing of the wound by providing a sterile, breathable and moist environment that facilitates granulation and epithelialization. This will then reduce the risk of infection, help the wound heal more quickly, and reduce scarring.
